Human Tour Guides for Mixed Reality: A Comparison of Capture and Display Techniques
Description
Virtual environments can be complex and overwhelming. In addition, when wearing a bulky head-mounted display one easily feels isolated from the real world. For my Master's thesis I investigated how humanoid embodied tour guides could be created to accompany and guide users in a Mixed Reality environment.
Year
2023
Contribution
all
Context
Masters Thesis at TU Dresden towards M.Sc. Computer Science and Media
Skills
Unreal Engine, Meta Quest, XR, Motion Capture
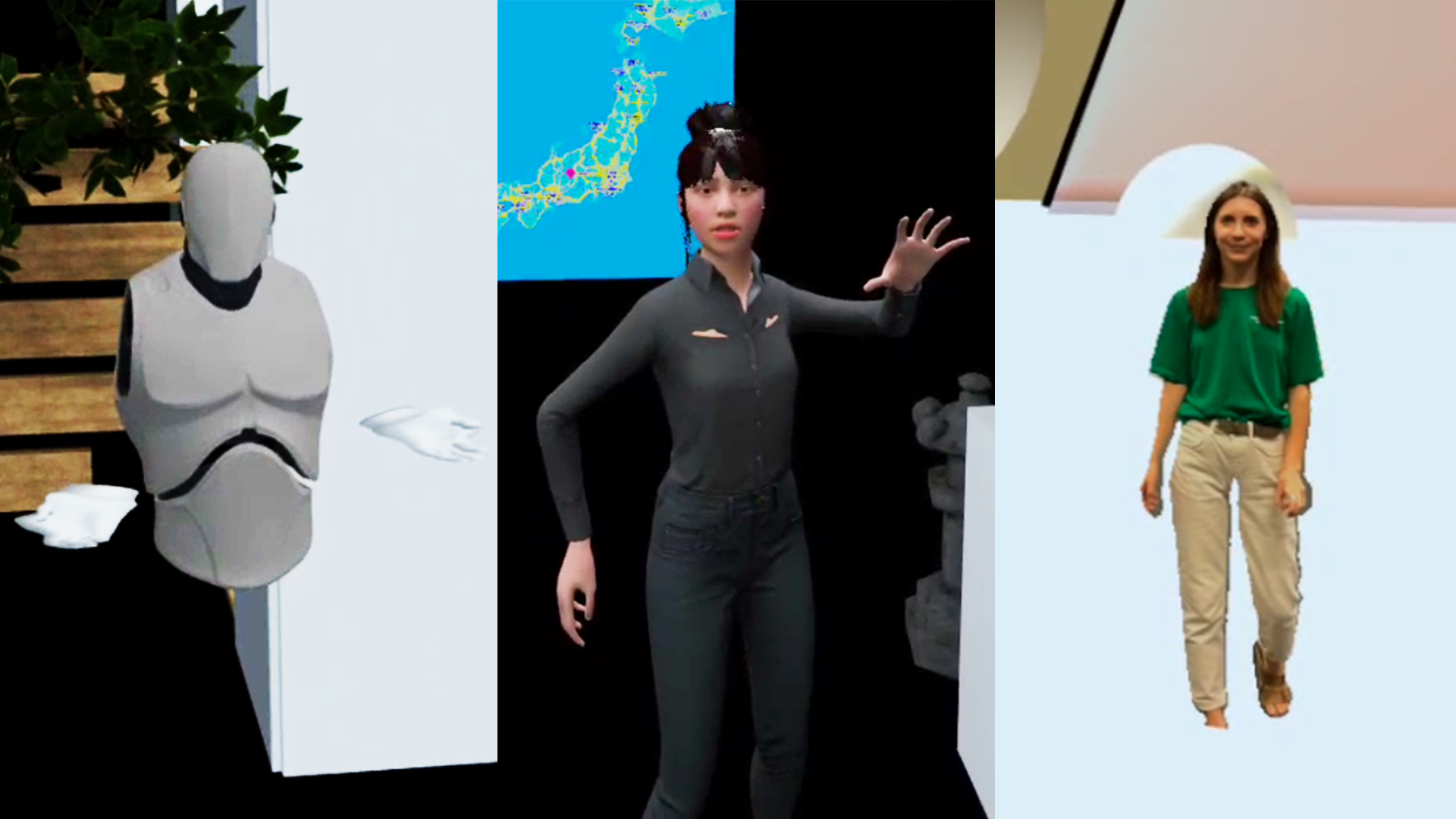

A guided Visit in a Mixed Reality Art Gallery
Working with UE4 and Meta's Quest Pro, I created a Mixed Reality art gallery prototype. I used the prototype as context to test three different representations of guides with varying degrees of visual realism. To simplify the creation process I looked at ways of recording real tour guides to transfer their behavioral realism onto the virtual guides. For example, I explored the Quest's body and face tracking to animate a MetaHuman. Through user testing, I then compared the representations towards Social Presence and overall user acceptance.

Use natural Communication and provide Company
Virtual environments can be complex and overwhelming. In addition, when wearing a bulky head-mounted display one easily feels isolated from the real world. For my Master's thesis I investigated how humanoid embodied tour guides could be created to accompany and guide users in a Mixed Reality environment. Furthermore, I was interested in how the guide could efficiently explain content by applying Joint Attention Mechanisms such as Pointing and Gaze direction supported by verbal terms. I aimed to increase Social Presence to provide a trustworthy company, mental support and increase the level of comfort.
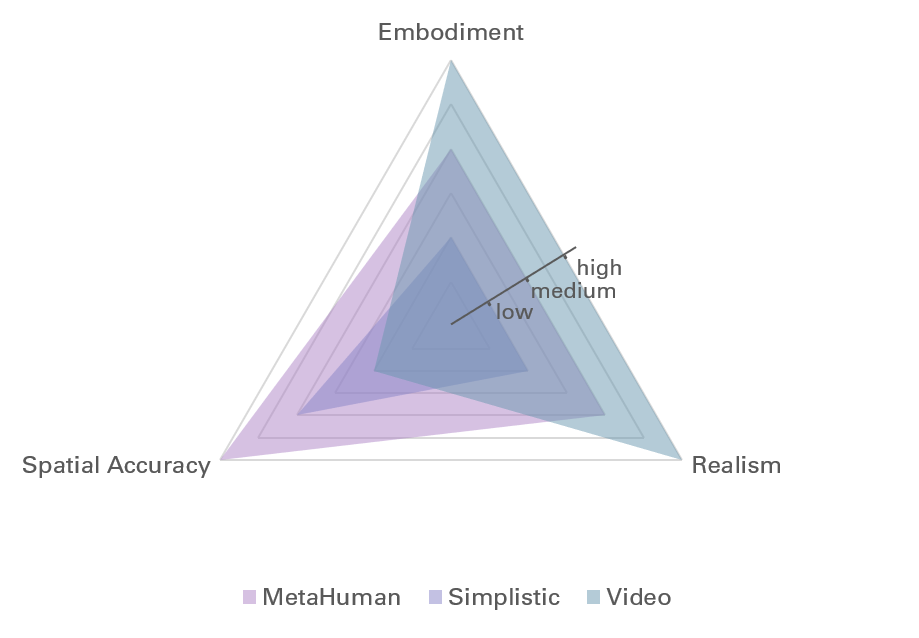
Provide the Guide with humanoid Characteristics
State-of-the-Art guidance varies in terms of visual realism, level of embodiment and how they integrate into the immersive environment (Spatial Accuracy). While I explicitly sought to compare different levels of visual realism, the characteristics of the representations I compared cover all degrees for each characteristic trait.
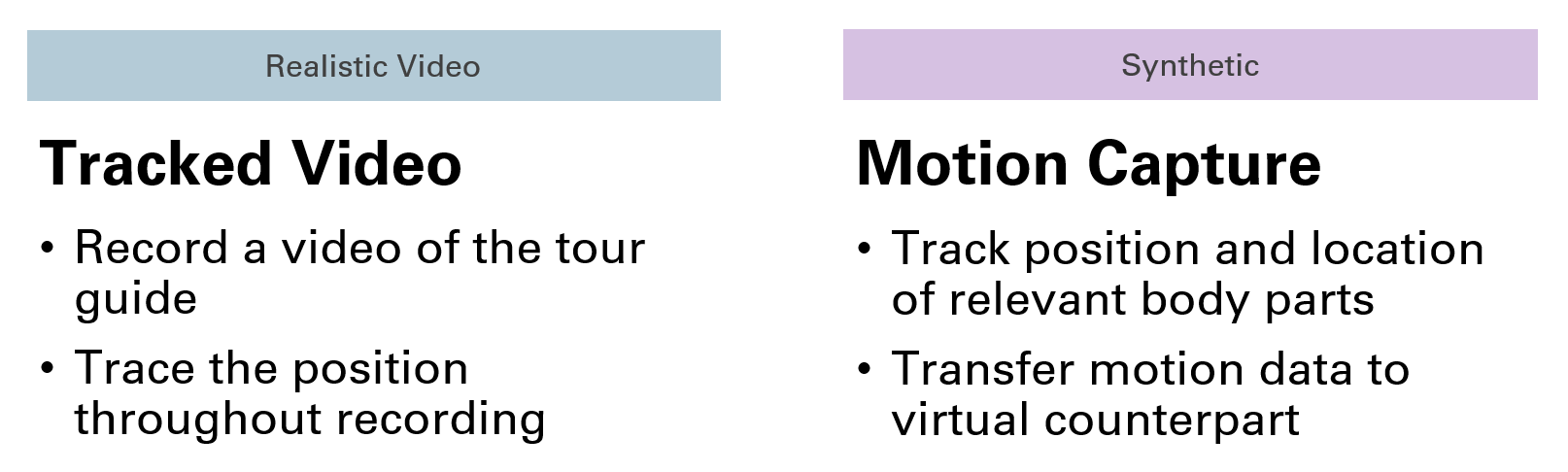
Simplify the Creation Process
It's way more convenient to just implement a simple text label or arrows as indicators to guide a user. But a virtual experience can profit a lot from an embodied guide. To make the creation of a humanoid guide accessible for everyone without any programming nor animation experience, I looked into different approaches. As I ended up comparing one video based guide and two synthetic guides I needed different approaches for recording.
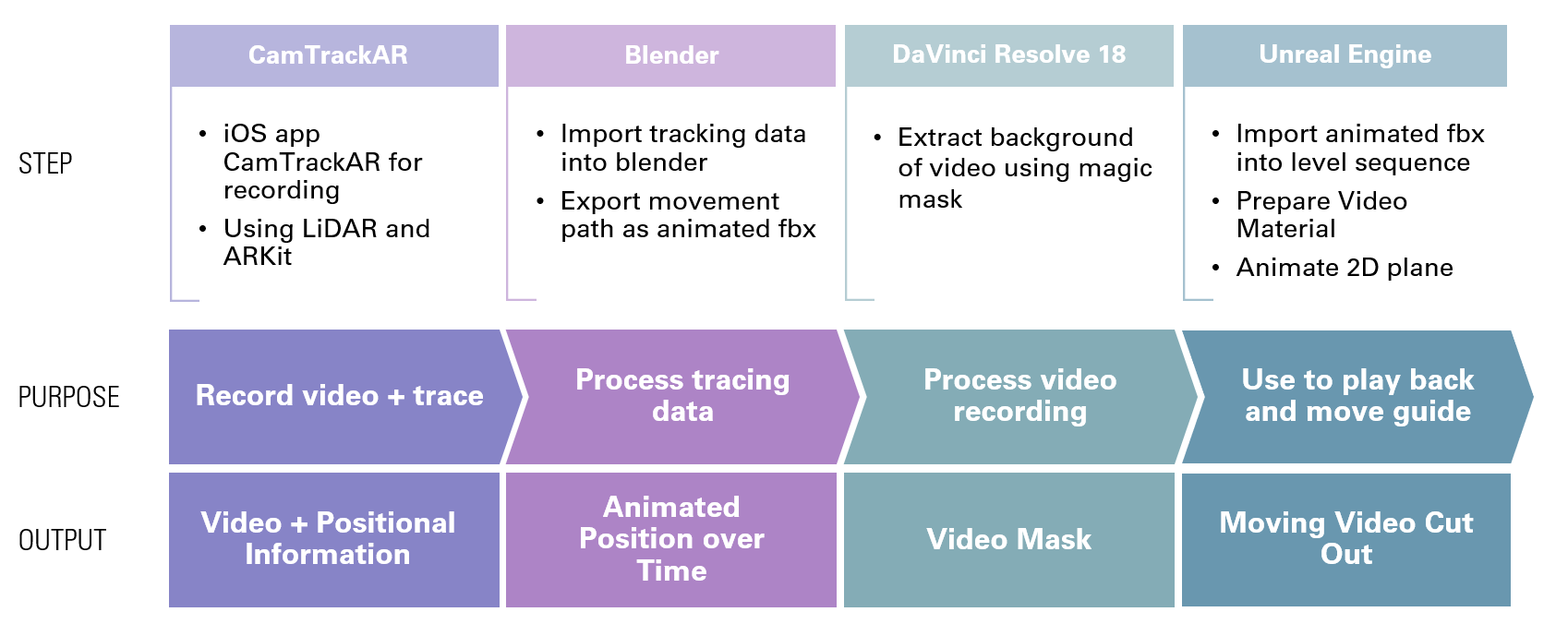
Recording the Video Guide
For the video guide I recorded a video using an iPad. The position of the iPad was tracked throughout the video recording to derivate the guide's position in space.
Recording the Synthetic Guides
I ended up using the Quest Pro's motion tracking capabilities to record hands, face and position of the guide.
Capture Motion from a Video
I explored different techniques to extract motion data from a single view image. However, none of the tested solutions did suffice to simultaneously track position in space, accurate hand gestures and facial expressions.
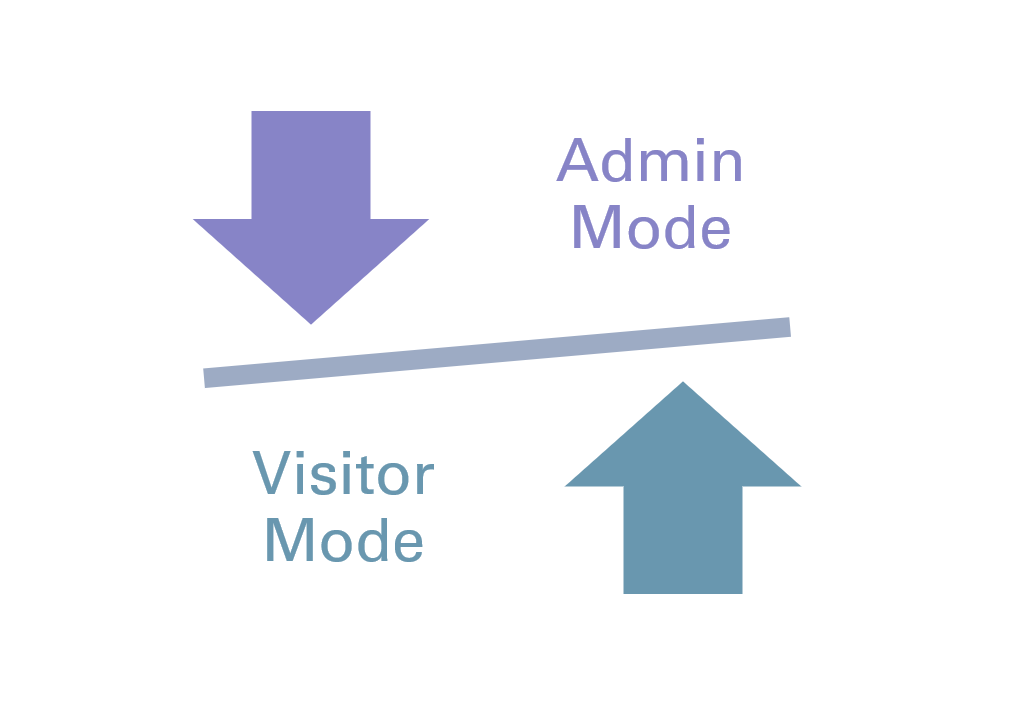
Mixed Reality Prototype
The MR Prototype I developed has two different modes: An admin Mode for recording a guided tour and a visitor mode to participate in a guided tour.

Interaction
I provided the user with a personal menu. Whenever a hand is rotated towards the face with all fingers stretched, the menu appears. This gesture is more comfortable and reliable than a 'looking-at-a-watch' gesture. The user does then interact with the menu by tapping the buttons.
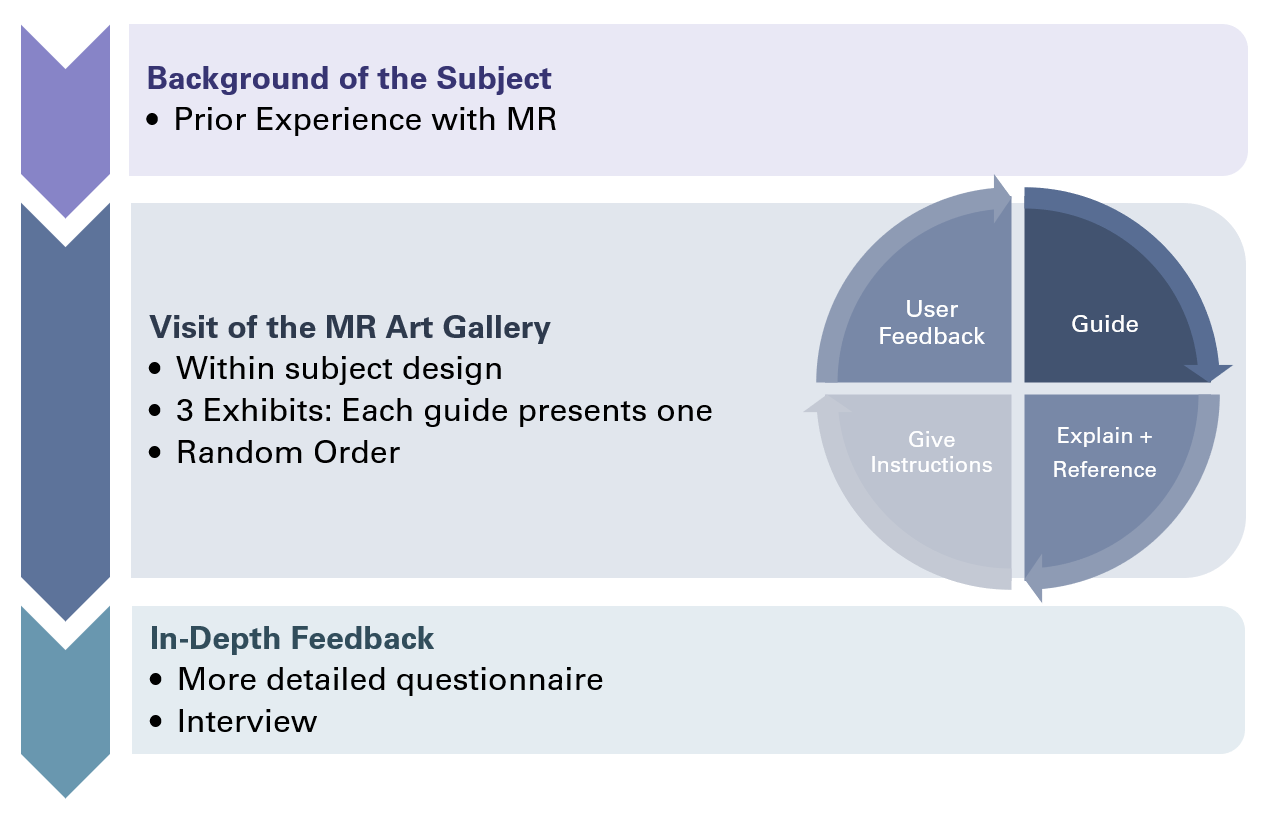
User Testing
I ran user tests to compare the guides. The graphic shows the testing procedure consisting of 3 steps.